Operations on Processes
Process operations refer to the actions or activities performed on processes in an operating system. These operations include creating, terminating, suspending, resuming, and communicating between processes. Operations on processes are crucial for managing and controlling the execution of programs in an operating system.
Operations on processes are fundamental to the functioning of operating systems, enabling effective flow of program execution and resource allocation. The lifecycle of a process includes several critical operations: creation, scheduling, blocking, preemption, and termination. Each operation plays a vital role In ensuring that processes are efficiently managed, allowing for multitasking and optimal resource utilization. In this article, we will discuss various operations on Process.
What is a Process?
A process is an activity of executing a program. It is a program under execution. Every process needs certain resources to complete its task. Processes are the programs that are dispatched from the ready state and are scheduled in the CPU for execution. PCB (Process Control Block) holds the context of the process. A process can create other processes which are known as Child Processes. The process takes more time to terminate, and it is isolated means it does not share the memory with any other process. The process can have the following states new, ready, running, waiting, terminated, and suspended.
Aiming for a top All India Rank in GATE CS/IT or GATE DA 2026? Our courses, led by experts like Khaleel Sir, Chandan Jha Sir, and Vijay Agarwal Sir, offer live classes, practice problems, doubt support, quizzes, and All India Mock Tests—all in one place.
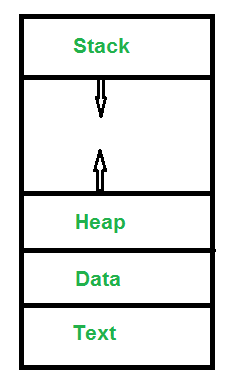
- Text : A Process, sometimes known as the Text Section, also includes the current activity represented by the value of the Program Counter .
- Stack : The stack contains temporary data, such as function parameters, returns addresses, and local variables.
- Data : Contains the global variable.
- Heap : Dynamically memory allocated to process during its run time.
Operation on a Process
The execution of a process is a complex activity. It involves various operations. Following are the operations that are performed while execution of a process:

1. Creation
This is the initial step of the process execution activity. Process creation means the construction of a new process for execution. This might be performed by the system, the user, or the old process itself. There are several events that lead to the process creation. Some of the such events are the following:
- When we start the computer, the system creates several background processes.
- A user may request to create a new process.
- A process can create a new process itself while executing.
- The batch system takes initiation of a batch job.
2. Scheduling/Dispatching
The event or activity in which the state of the process is changed from ready to run. It means the operating system puts the process from the ready state into the running state. Dispatching is done by the operating system when the resources are free or the process has higher priority than the ongoing process. There are various other cases in which the process in the running state is preempted and the process in the ready state is dispatched by the operating system.
3. Blocking
When a process invokes an input-output system call that blocks the process, and operating system is put in block mode. Block mode is basically a mode where the process waits for input-output. Hence on the demand of the process itself, the operating system blocks the process and dispatches another process to the processor. Hence, in process-blocking operations, the operating system puts the process in a ‘waiting’ state.
4. Preemption
When a timeout occurs that means the process hadn’t been terminated in the allotted time interval and the next process is ready to execute, then the operating system preempts the process. This operation is only valid where CPU scheduling supports preemption. Basically, this happens in priority scheduling where on the incoming of high priority process the ongoing process is preempted. Hence, in process preemption operation, the operating system puts the process in a ‘ready’ state.
5. Process Termination
Process termination is the activity of ending the process. In other words, process termination is the relaxation of computer resources taken by the process for the execution. Like creation, in termination also there may be several events that may lead to the process of termination. Some of them are:
- The process completes its execution fully and it indicates to the OS that it has finished.
- The operating system itself terminates the process due to service errors.
- There may be a problem in hardware that terminates the process.
Conclusion
Operations on processes are crucial for managing and controlling program execution in an operating system. These activities, which include creation, scheduling, blocking, preemption, and termination, allow for more efficient use of system resources and guarantee that processes run smoothly. Understanding these procedures is critical to improving system performance and dependability.so these processes help our computers do many things at once without crashing or slowing down.
Comments
Post a Comment